WHAT IS PHISHING? AND HOW DO I KEEP MYSELF SAFE?
Avoid Falling Prey to Phishing Scams:
In the past year we have been transitioning our lives online, from working remotely to taking classes online, the majority of our daily activities now revolve around our digital workspace. This means that it has become increasingly important to consider the security of our workspace and if we are engaging in safe cyber security practices.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is an online scam where cybercriminals impersonate legitimate organizations in an attempt to gain access to your personal information. Phishing can take many forms, but the most common phishing scams are conducted through email, text message, or advertisements. Typically what happens is that phishing messages contain a link to an external ‘company website’ where you are asked to fill out your information. However, these websites are fakes and the information ends up in the hands of cybercriminals. These cybercriminals will then either use the information to impersonate the victim and conduct fraudulent activity (i.e., apply for credit cards, loans, etc) or sell it to other cybercriminals on the Dark Web.
The Rise of Phishing
In 2020, phishing exploded as the majority of the world had to close down due to the pandemic. Cybercriminals recognized that working remotely would mean that more people would be online and thus more likely to fall prey to online scams. Compared to 2019, phishing increased by 42% in 2020 and is still on the rise in 2021. The monumental rise in phishing scams shows no signs of slowing down. It is more important than ever to be aware of these scams and keep yourself safe.
How to Spot a Phishing Scam:
1. Look at the Email Address or the Sender
Check the email address that the message is coming from, not just the name of the sender. Always look to see if the domain name of the email (the part after the @ symbol) matches with the organization’s domain name. No legitimate companies will send you emails from their gmail (@gmail.com) or other non-professional accounts. Also check for misspellings in the domain name, since anyone can purchase a domain name from a register, cybercriminals may purchase one to make it seem like a legitimate email.
2. Check if it includes suspicious attachments or links
Some attachments can be infected and contain malware, an email may ask you to open something that seems like a legitimate document (e.g. an invoice) but actually will infect your systems once you open it. You should never open an attachment unless you are absolutely certain that it is from a legitimate party. If you are ever unsure, try contacting the sender through a different mode of communication (don’t reply to the email) and ask to verify that they were the ones who sent the attachment.
It is generally a good rule of thumb to not click on any suspicious links that you find in your emails. These links can lead you to a spoofed or fake website designed by cybercriminals to look legitimate. Rather than clicking on any links, navigate to the webpage via a search engine or another secured method. If the message was legitimate, you should receive the same prompt or information once you reach the legitimate website.
3. Are there Grammatical Errors?
If the email is poorly written then this could be a red flag that it is a potential scam. This could indicate a potential for a malicious phishing attempt by a cybercriminal that does not speak fluent English. This is not to say any message with an error in it is a scam, but it does mean that you should examine the contents of the message more carefully.
Was the mistake a common typo (e.g. hitting an adjacent key) or was it a large grammatical error that a native English speaker would not make (e.g. misusing certain words)? Is the tone of the message consistent with other ones that you have received from your sender? These are all important questions to consider when evaluating the legitimacy of the email. Remember, if you are ever unsure, the best thing to do is contact that person via another platform to ensure the legitimacy of the message. It is always better to be safe than sorry.
4. Is there a sense of urgency or a threat in the message?
Is the message sending you a threat or an urgent request for action? This is a major indication that it could be a malicious message. The senders are taking advantage of the sense of urgency so that you will not be as careful in reading and evaluating the message. Many victims will panic and give out their confidential information without considering the implications of a malicious actor. Always take the time to think and look over the message before responding to an urgent or threatening email.
5. Is it too good to be true?
If the message is letting you know that you have won some type of ‘prize’ or ‘gift’ from an unknown contest or deal, it is likely a phishing scam. They hope to draw you in and capture your attention with the promise of a prize in exchange for personal information. If the contest was unknown to you and you do not know the organization or the organizer, then it is likely a scam.
Examples of a Phishing Scam
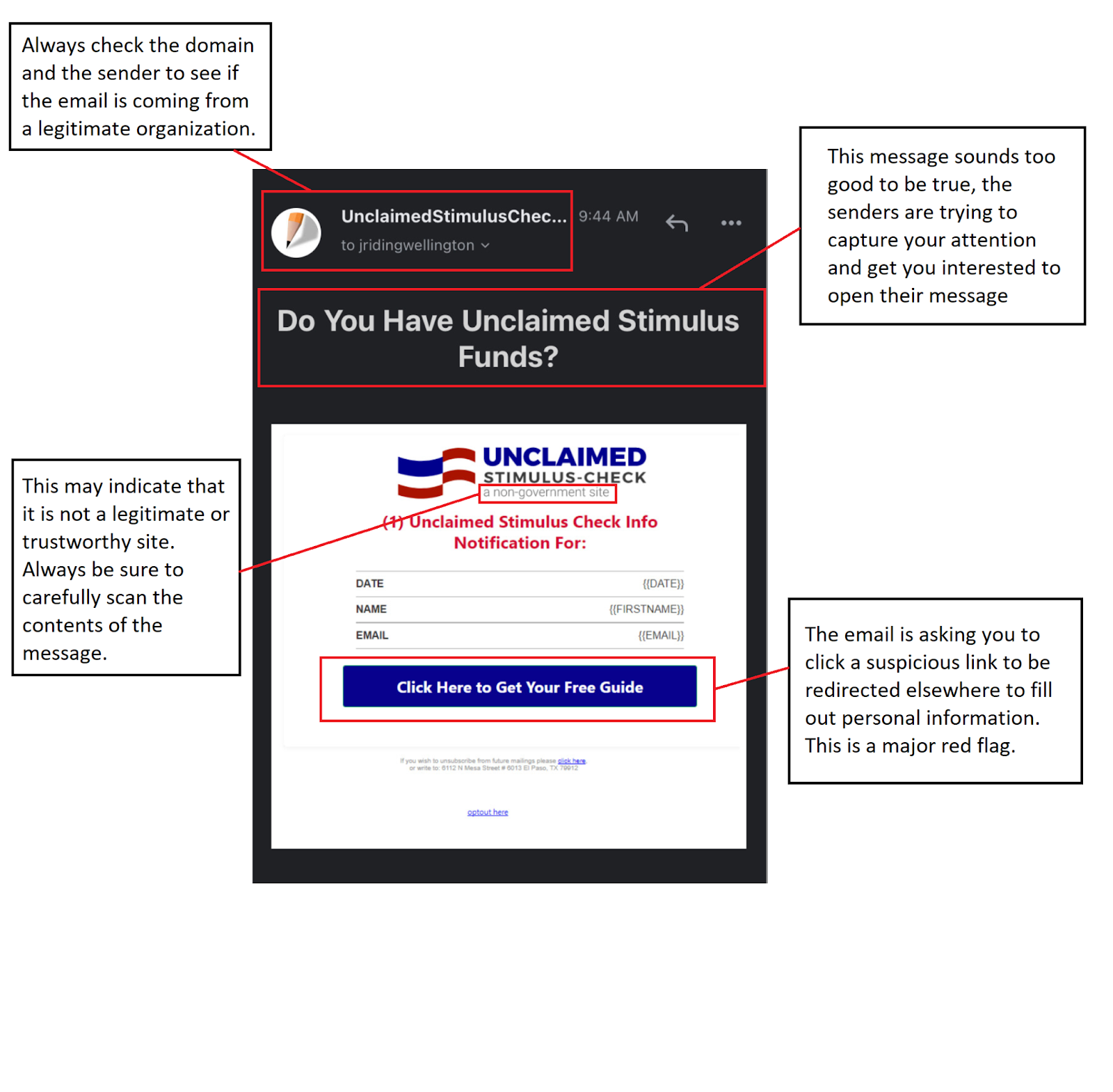
What Else Can You Do?
With next-level email security you won't have to worry about detecting phishing scams yourself. We monitor all incoming emails for potentially malicious links and attachments. If we find anything even remotely suspicious, you'll be the first to know.
Some of the incoming malicious emails will be blocked completely, while others will show up still in your inbox with a notification stating that there may be malicious phishing content within the message.
We also provide monthly reporting which will allow our clients to see exactly how many incoming phishing emails they were able to divert.
Find out more here or at www.cyberunit.com
